Stacks
A stack is a collection of objects that are inserted and removed according to the last-in, first-out (LIFO) principle. Popular uses of stacks are for "back" and "undo" operations in browsers and editors.
In general the LIFO protocol allows the stack to be used as a tool for reversing a data sequence, matching tags, parenthesis etc.
Some common methods supported by a stack are:
stack.push(e)- add an elementeto the top of a stackstack.pop()- remove and return the top elements from a stackstack.top()- return the top element of a stackstack.is_empty()- check if stack is emptylen(stack)- the number of elements in a stack
Simple Array-Based Stacks
We can implements stacks easily by using a list in Python.
Look at Adapter Pattern to get an example of a stack implementation using lists.
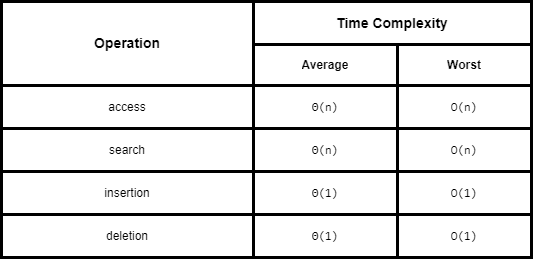
Efficiencies
Space Complexity: O(n)
Time Complexities:
References
-
Skiena, Steven S.. (2008). The Algorithm Design Manual, 2nd ed. (2). : Springer Publishing Company. ↩
-
Goodrich, M. T., Tamassia, R., & Goldwasser, M. H. (2013). Data Structures and Algorithms in Python (1st ed.). Wiley Publishing. ↩
-
Cormen, T. H., Leiserson, C. E., & Rivest, R. L. (1990). Introduction to algorithms. Cambridge, Mass. : New York, MIT Press. ↩