Queues and Deques
Queues
A queue is a collection of objects that are inserted and removed according to the first-in, first-out (FIFO) principle. Elements can be inserted at any time, but only the elements that has been in the queue the longest can be next removed.
Some common methods supported by a queue are:
queue.enqueue(e)- add an elementeto the back of a queuequeue.dequeue()- remove and return the first element from a stackqueue.first()- return the first element of a stackqueue.is_empty()- check if queue is emptylen(queue)- the number of elements in a queue
Array-Based Queue Implementation
Utilizing a list for a queue would be very inefficient - this is because pop(0) i.e. a pop on a non-default index causes a loop to be executed that shifts all elements beyon the index to te left. This would cause the worst-case behavior of O(n) time.
Therefore we need to implement a queue using a circular array with the following logic:
- initialize a
listwith a fixed size that is larger than the actual number of elements t be ever added tot he queue - define
frontas the index of the "first" element of a queue - enqueue items to the index calculated by
(front + size) % capacityof the queue - for example for a queue of size 3, enqueue of [2, 1, 4] would be built as following: [2, None, None] -> [2, 1, None] -> [2, 1, 4]
- then following dequeue operations will happen like so: [None, 1, 4] and front = 1 -> [None, None, 4] and front = 2 etc.
- whenever the size of the queue is equal to its capacity, resize it to be double the capacity, and whenever the size is ¼th of the capacity, resize it to be half the capacity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 | |
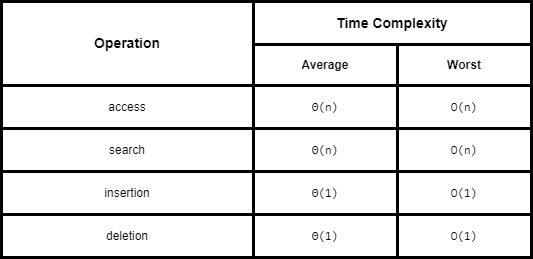
Efficiencies
Space Complexity: O(n)
Time Complexities:
Dequeue - Double-Ended Queues
A queue like data structure that supports insertion and deletion from both the front and back of the queue.
An implementation of this is available through the deque class in Python in the standard collections module.
Array-Based Deqeue Implementation
We can implement a deque in a similar way as the Queue. The main modifications are:
- adding a pointer to the last element as
.last()wherelast = (self._front + self._size - 1) % len(self._data) - ability to add and remove from the back of the queue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 | |
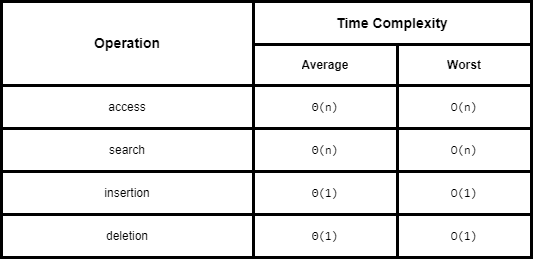
Efficiencies
Space Complexity: O(n)
Time Complexities:
References
-
Skiena, Steven S.. (2008). The Algorithm Design Manual, 2nd ed. (2). : Springer Publishing Company. ↩
-
Goodrich, M. T., Tamassia, R., & Goldwasser, M. H. (2013). Data Structures and Algorithms in Python (1st ed.). Wiley Publishing. ↩
-
Cormen, T. H., Leiserson, C. E., & Rivest, R. L. (1990). Introduction to algorithms. Cambridge, Mass. : New York, MIT Press. ↩